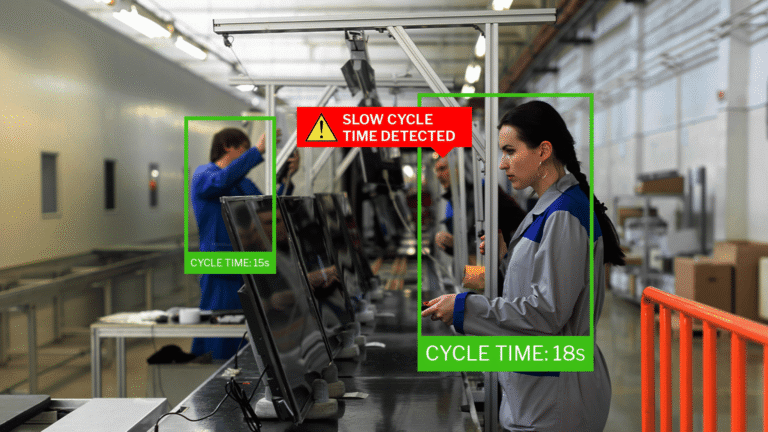
Quality control is a critical component of manufacturing, ensuring that products meet industry standards, customer expectations, and regulatory requirements. Traditional quality control methods, such as manual inspections and sample testing, have been widely used but often fall short in terms of speed, accuracy, and scalability. As production lines become more complex and the demand for precision increases, manufacturers are turning to advanced technologies to enhance quality assurance.
Computer vision, a field of artificial intelligence that enables machines to interpret and analyze visual data, is transforming the way manufacturers approach quality control. By integrating high-resolution cameras, machine learning algorithms, and real-time processing, computer vision systems can detect defects, identify inconsistencies, and automate quality assessments with unparalleled accuracy.
In this blog post, we’ll explore how computer vision enhances quality assurance, its key applications across industries, and the benefits of adopting this technology in modern manufacturing.
How Computer Vision Enhances Quality Control
A computer vision system for manufacturing quality control typically consists of three main components:
- Cameras and Sensors: Industrial-grade cameras capture high-resolution images or videos of products moving along the production line. Sensors provide additional data, such as depth and infrared imaging, to enhance accuracy.
- AI and Machine Learning Models: Advanced AI algorithms, including generative AI, analyze images to detect defects, anomalies, or inconsistencies. These models continuously improve by learning from new data.
- Edge and Cloud Computing: Edge computing processes data locally for real-time decision-making, while cloud computing enables large-scale data storage, model training, and analytics for continuous improvement.
Computer vision systems, such as smart AI assembly solutions, perform several essential quality control tasks, including:
- Object Detection: Identifying specific products, components, or packaging on the production line.
- Defect Identification: Detecting surface defects, incorrect assembly, or missing parts at a micro level.
- Pattern Recognition: Analyzing textures, shapes, or color variations to ensure product consistency.
Deep learning, a subset of AI, further enhances these capabilities by training models to recognize even subtle deviations from the standard, leading to increased accuracy and fewer false positives.
Benefits and Applications of Computer Vision in Quality Control
As advancements in AI and robotics in industry accelerate, computer vision is transforming manufacturing quality control in several key ways:
- Higher Accuracy: AI-driven systems can detect even the smallest defects, significantly reducing human error.
- Faster Inspections: Real-time image processing enables instant defect identification and rapid response.
- Cost Savings: By minimizing waste, reducing rework, and decreasing reliance on manual inspections, companies can lower operational costs.
- Scalability and Consistency: Ensures uniform quality checks across multiple production lines—without fatigue or variation.
- Regulatory Compliance: Automates critical safety and compliance inspections for industries such as pharmaceuticals, automotive, and food manufacturing.
Implementing Computer Vision in Manufacturing
Integrating computer vision into manufacturing requires a combination of hardware, software, and system integration to achieve seamless, real-time quality control. Below are the key components and considerations for successful implementation.
1. Key Hardware Components
Computer vision relies on specialized hardware to capture and process images in real time. Industrial-grade cameras and sensors provide high-resolution visuals, while technologies such as infrared and thermal imaging enhance defect detection. To handle large volumes of image data efficiently, manufacturers use GPUs and edge computing devices, which enable high-speed processing and reduce latency for real-time decision-making.
2. Software and AI Models
Choosing the right software and AI models is essential for optimizing performance and maintaining affordability. Manufacturers can leverage open-source frameworks like OpenCV and TensorFlow for flexibility and customization, or opt for proprietary solutions that offer pre-trained models, enterprise support, and seamless integration.
Much like students search for affordable engineering colleges to get quality education, manufacturers seek affordable AI solutions that deliver maximum efficiency. AI-powered deep learning models not only enhance defect detection but also continuously improve accuracy over time.
When selecting AI-driven quality control systems, balancing performance with affordability is key—just as students evaluate colleges for the best return on investment. With the right tools, manufacturers can achieve cost-effective, precision-driven quality control, mirroring how affordable education empowers future engineers.
3. Integration with Existing Manufacturing Systems
Seamless integration with existing manufacturing systems ensures that computer vision enhances overall production efficiency. Key integration technologies include:
- Internet of Things (IoT): IoT-enabled cameras and sensors collect and transmit real-time data, enabling automated monitoring and analytics.
- SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition): Computer vision systems integrate with SCADA to automate quality control workflows and reduce human intervention.
- ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning): Connecting computer vision with ERP systems helps manufacturers track defect rates, optimize production efficiency, and ensure compliance.
4. Cloud vs. Edge Computing for Real-Time Processing
Selecting the right computing infrastructure is essential for effective implementation.
- Edge computing enables real-time defect detection by processing data locally, reducing reliance on cloud connectivity and minimizing delays.
- Cloud computing supports large-scale data storage, AI model training, and in-depth analytics but may introduce latency in real-time operations.
A well-designed implementation strategy ensures that computer vision seamlessly integrates with manufacturing operations, optimizing quality control and enhancing production efficiency.
Improve Your Quality Control Manufacturing
In conclusion, computer vision is revolutionizing quality control in manufacturing by enhancing accuracy, efficiency, and scalability. Traditional inspection methods are often slow and prone to human error, whereas AI-powered vision systems detect defects in real time, reducing waste and ensuring product consistency.
By leveraging industrial cameras, machine learning models, and edge computing, manufacturers can automate quality assessments, improve compliance, and optimize production workflows. As industries continue to embrace AI-driven solutions, integrating computer vision will be essential for maintaining a competitive edge. Manufacturers should explore real-time quality control innovations to enhance productivity, reduce costs, and meet ever-evolving market demands.