Key Takeaways
- Definition: Quality 4.0 integrates AI and data with quality management to predict defects rather than detect them.
- Core Steps: The transition requires digitising paper records, connecting IoT sensors, and applying Vision AI.
- India Context: Indian manufacturers are leveraging Smart Factory initiatives to leapfrog legacy constraints.
- Major Pitfalls: Success depends on eliminating data silos and retrofitting legacy machines.
The manufacturing landscape in India is undergoing a seismic shift. As the Make in India initiative gains momentum, the pressure to deliver zero-defect products at scale has never been higher. This is where Quality 4.0 implementation becomes the differentiator between surviving and thriving. By integrating Industry 4.0 technologies with traditional quality excellence, manufacturers can transition from reactive problem-solving to proactive process optimisation.
What is Quality 4.0?
Quality 4.0 is the application of Industry 4.0 technologies—specifically Artificial Intelligence (AI), Machine Learning (ML), and Big Data analytics—to traditional quality management practices.
Unlike traditional methods that rely on retrospective inspection, Quality 4.0 uses real-time data to predict failures before they occur, ensuring continuous improvement across the entire value chain. It represents a shift from human-dependent checks to automated, data-driven intelligence.
The Strategic Importance of Digital Transformation in Manufacturing
For Indian manufacturers, adopting a Smart Factory approach is no longer optional. Global supply chains demand rigorous adherence to standards, and manual processes simply cannot keep pace. Quality 4.0 implementation allows factories to reduce scrap rates, lower warranty costs, and improve overall equipment effectiveness (OEE). Research indicates that successful implementation can reduce the cost of quality by up to 20–30% while significantly boosting throughput.
Step-by-Step Guide to Quality 4.0 Implementation
Transitioning to a smart quality system does not require rebuilding your factory from scratch. It requires a logical, phased approach.
Step 1: Digitise Data (Eliminate Paper Sheets)
The first hurdle in Quality 4.0 implementation is reliance on analogue data. You cannot analyse what you cannot read digitally. Many factories in India still rely on clipboards and paper checklists for quality logs. This creates a “black hole” of information where data is recorded but rarely analysed in time to make a difference.
Action: Immediately stop using paper sheets for inspection logs. Deploy tablets or mobile interfaces on the shop floor. By digitising this data at the source, you create a historical record that is instantly searchable and ready for analysis.
Step 2: Connect Sensors (IoT Integration)
Once manual data entry is digitised, the next step is to capture machine data automatically. This involves the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT). Machines generate vast amounts of data regarding temperature, vibration, pressure, and speed, which are often ignored until a breakdown occurs.
Action: Retrofit critical assets with IoT sensors. These sensors act as the nervous system of the factory, streaming real-time performance data to a central dashboard. This connectivity enables condition-based monitoring, ensuring that quality parameters are maintained within strict tolerances without human intervention.
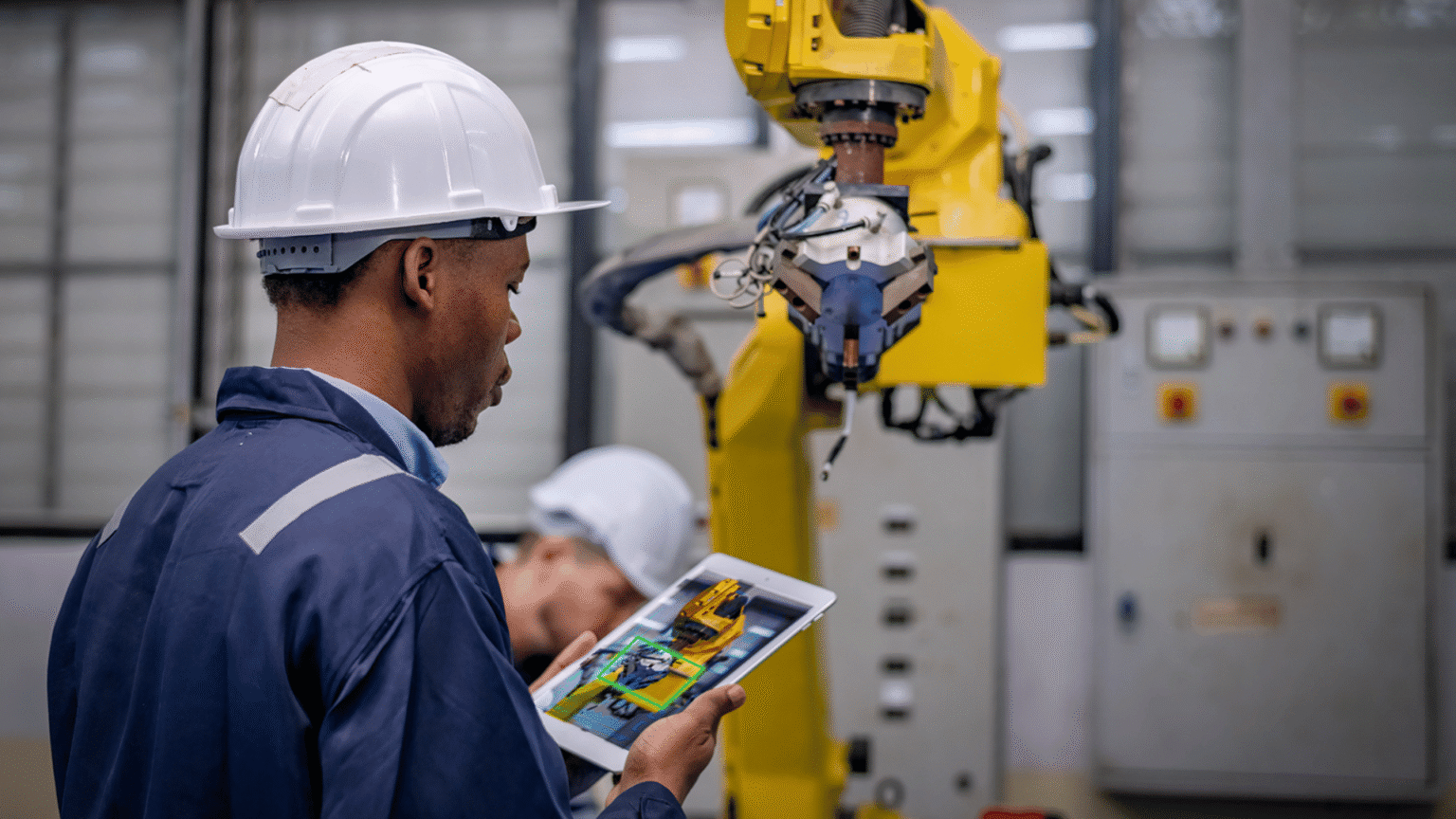
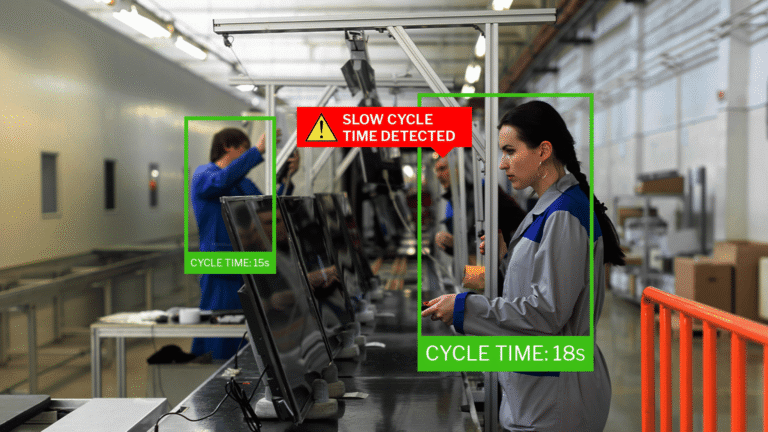
Step 3: Apply Vision AI (Hypervise)
The pinnacle of AI quality control is the application of visual intelligence. While sensors detect internal machine states, they cannot always “see” surface defects or assembly errors. This is where Vision AI comes into play.
Action: Implement computer vision systems to Hypervise your production line. These systems use high-definition cameras and deep learning algorithms to inspect 100% of products at line speed. Unlike human inspectors, who fatigue over time, Vision AI maintains consistent accuracy, detecting microscopic anomalies that the human eye might miss. For a practical look at how this technology works, you can view a technology demo here.
Comparing Traditional QC vs. Quality 4.0
To understand the value proposition, it is essential to compare the traditional approach with the modern Quality 4.0 framework.
| Feature | Traditional Quality Control | Quality 4.0 Implementation |
| Data Source | Paper sheets, manual entry, isolated spreadsheets | Cloud-based, real-time IoT sensors, digital logs |
| Inspection Method | Sampling (checking 1 in 100 parts) | 100% inspection via AI quality control |
| Response Time | Reactive (fix after failure) | Predictive (fix before failure) |
| Traceability | Difficult, time-consuming manual searches | Instant, end-to-end digital thread |
| Cost Impact | High scrap and rework costs | Optimised yield, reduced waste |
Common Pitfalls in Quality 4.0 Implementation
Even with the best technology, projects can fail if foundational issues are ignored. Two specific challenges plague Indian manufacturers:
- Data Silos
A major barrier is the existence of data silos. This occurs when the quality department’s data does not communicate with production or maintenance systems. For Quality 4.0 implementation to work, data must flow freely across the organisation. If your Vision AI detects a defect, that data must instantly alert both the production manager and the maintenance team. - Legacy Machines
Many factories operate robust but older machinery that lacks native digital connectivity. A common misconception is that you need new machines to become smart. This is false. The real pitfall lies in failing to retrofit these legacy machines with external sensors. Ignoring legacy equipment creates blind spots in your quality data ecosystem.
Conclusion
Implementing Quality 4.0 is a journey of digital transformation in manufacturing that moves an organisation from reactive firefighting to intelligent prediction. By digitising data, connecting IoT sensors, and utilising Vision AI to Hypervise production, Indian manufacturers can achieve world-class quality standards.
Frequently Asked Questions
The biggest challenge is often cultural rather than technical. Moving from paper-based, manual processes to digital, data-driven workflows requires strong change management. Additionally, breaking down data silos between departments is critical for success.
Yes. You do not need to replace expensive machinery. By using retrofit IoT sensors and external Vision AI cameras, legacy machines can be effectively integrated into a modern Quality 4.0 framework.
Traditional machine vision relies on rule-based programming (for example, “if length < 5 mm, reject”). AI Quality Control uses deep learning to understand what a “good” part looks like, enabling it to identify complex and variable defects (such as scratches or texture variations) that rule-based systems often miss.
While there is an initial investment, the ROI is typically rapid due to reduced scrap and rework. Cloud-based solutions and scalable IoT sensors have made these technologies accessible even for Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs) in India.